Hot forging
Hot forging is the shaping of a piece of metal carried at a suitable temperature and plastically deformed between two dies in which the impression of the desired part has been cut, close to the finished product considerably reducing the machining work
This deformation is effected by creeping the metal between the die and the punch, this transformation allows very large displacements of metal, refines the starting metallurgical grain, causes strain hardening, creates a favorable linear drawing by considerably improving the mechanical characteristics of the metal. piece.
The base metal is generally a bar of round or profiled section, scored by sawing in order to have the volume of the piece increased by an excess to guarantee the complete filling of the shape and create a burr which will be eliminated by cutting.
The advantages of hot forging:
- Approximate shape of finished product which limits the use of machining in finishing.
- Economy of material implementation and time.
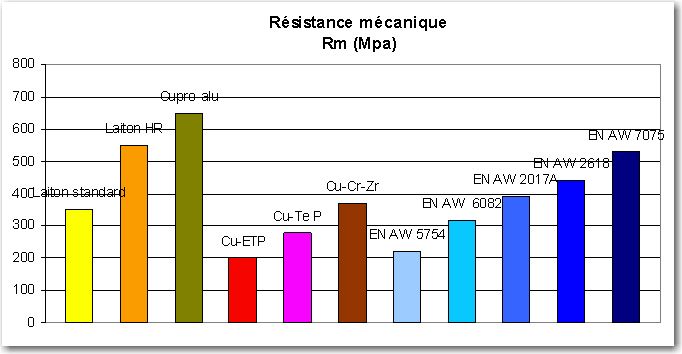
- Resistance, homogeneity, precision.
- Reproducibility and reliability of the manufacturing process.
- Surface finish without porosity allowing many finishes such as polishing or surface treatments
| Material | Resistance corrosion | Welding | Riveting | Sealing | Machining | Deformation | Surface treatment | Other |
| CuZn40Pb2 | B | B | C | A | A | A polishing A chroming A plating A tinning A painting |
||
| CuZn37Mn3Al2 PbSi |
A | D | A | A chroming A plating A tinning |
||||
| CuAl9Ni3Fe2 | A | B | A | C | A chroming A plating A tinning |
B frictions | ||
| Cu-ETP | B | B | A | A | C | A silver | ||
| Cu-Te P | B | C | B | A | B | |||
| Cu-Cr-Zr | B | B | A | C | C | |||
| AlCu4MgSi | D | C | D | A | B | C anodisation | ||
| AlCu2Mg1.5 Ni |
D | C | D | A | C | C anodisation | ||
| AlMg3 | A | A | C | A | C | A anodisation | ||
| AlSi1MgMn | B | B | D | A | C | A anodisation | ||
| AlZn5.5MgCu | D | C | D | A | B | B anodisation |
Aptitudes : A = Excellent, B = Good, C = Fair, D = Bad
M.C.T. Can not be in any way responsible for the exploitation of the indicative data of this commercial document